Selective Laser Sintering is one of the methods used by 3D printers to create 3D objects. SLS is also called Additive Manufacturing or simply 3D printing. The word “Sintering” means to create something by atomically fusing powders. Sintering was not invented for 3D printing but has been around for centuries used in traditional industries like brick making, porcelain production and even in creating jewelry. The inventors of SLS thought why not take an ancient concept like sintering and implement it in one of the most modern technologies around. If you can create a solid brick from fused powders why not use those powders as the “ink” in a printer to create a 3D object. The next step was to figure out how to fuse the powders into a solid form at some point in the printing process.
SLS was developed and patented in the 1980s by student Carl Deckard and his University of Texas mechanical engineering professor, Joe Beaman. The two went on to establish one of the original 3D start-ups, Desk Top Manufacturing (DTM) Corps which was later sold to 3D Systems who had developed a different method of 3D printing called stereolithography.
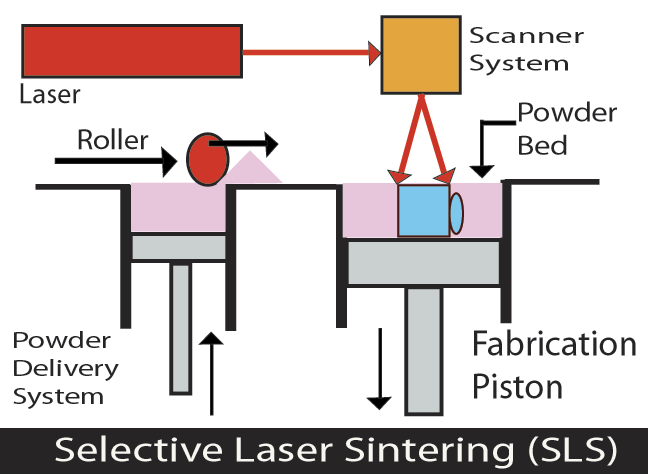
How Does SLS Work?
Like all 3D printed objects the first phase is to design the object using a computer program – a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) file. The files are then converted into a .STL format which 3D printers can “read.” A .STL file (Standard Tessellation Language) describes only the surface geometry of a 3D object without reference to it color, texture or common CAD model attributes. The printer takes thin thread-like thermoplastic material and a support material and creates thin layers of cross0sections of the object.
The 3D printer is then loaded with your chosen powdered materials. Tiny particles of plastic, nylon, glass, ceramics or metal are fused together using heat emitted by a high powered laser. When the elements fuse they form the finished 3D shape. The .STL file is sent to the 3D printer to tell it what to print. The powder is ejected onto the printer platform laying a thin cross-section of the object onto the powder. The printer’s laser heats the powder to just below boiling point or just above boiling point to melt the powders together. The powders are fused into a solid object. It repeats this process with consecutive layers, each time the platform is lowered slightly(less than 0.1mm) so that the 3D object is built from the bottom up. The object must then be left to cool.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SLS Over Other Methods of 3D Printing
SLS is a convenient and affordable way of making prototypes in industry. It can be used in 3D printers in businesses, industry and by hobbyists. The resulting objects require very little additional work. They don’t usually need to be finished by sanding. The SLS printing method does not require that the object being created is supported in any way during the process. Stereolithography and Fused Deposition Modeling take longer and usually require support of the object as it is being created. SLS is preferable for industry and not for home 3D printers as it required a high-powered laser and is potentially more dangerous than other methods like FDM.
3D-Print Today is an online news magazine bringing you up to date on all the latest news from the 3D Printing Industry. We work hard on finding interesting and unique news stories and fresh trends on the market.
Our online magazine provides a compelling blend of daily articles, fresh news, blog posts and opinions, as well as videos and visuals across all platforms through our main website, our mobile application and the social media network; all contains the detailed information and up to date news, for you to discover the amazing world of 3D Printing.
245 Greene Street
New York, NY 10012